A quick peek at the common applications of medical chillers.
Medical chillers are most commonly used to keep equipment running smoothly. They are also used to lower patients’ body temperatures during certain procedures and to keep medical samples at proper temperatures.
Chillers are used in various applications throughout the medical industry. Often, proper chilling in medical applications means keeping life-saving equipment running smoothly; there is very little room for error. It is therefore extremely important that medical facilities take great care in implementing cooing solutions.
What are medical chillers used for?
Typically medical chillers are used to perform one of the following three functions:
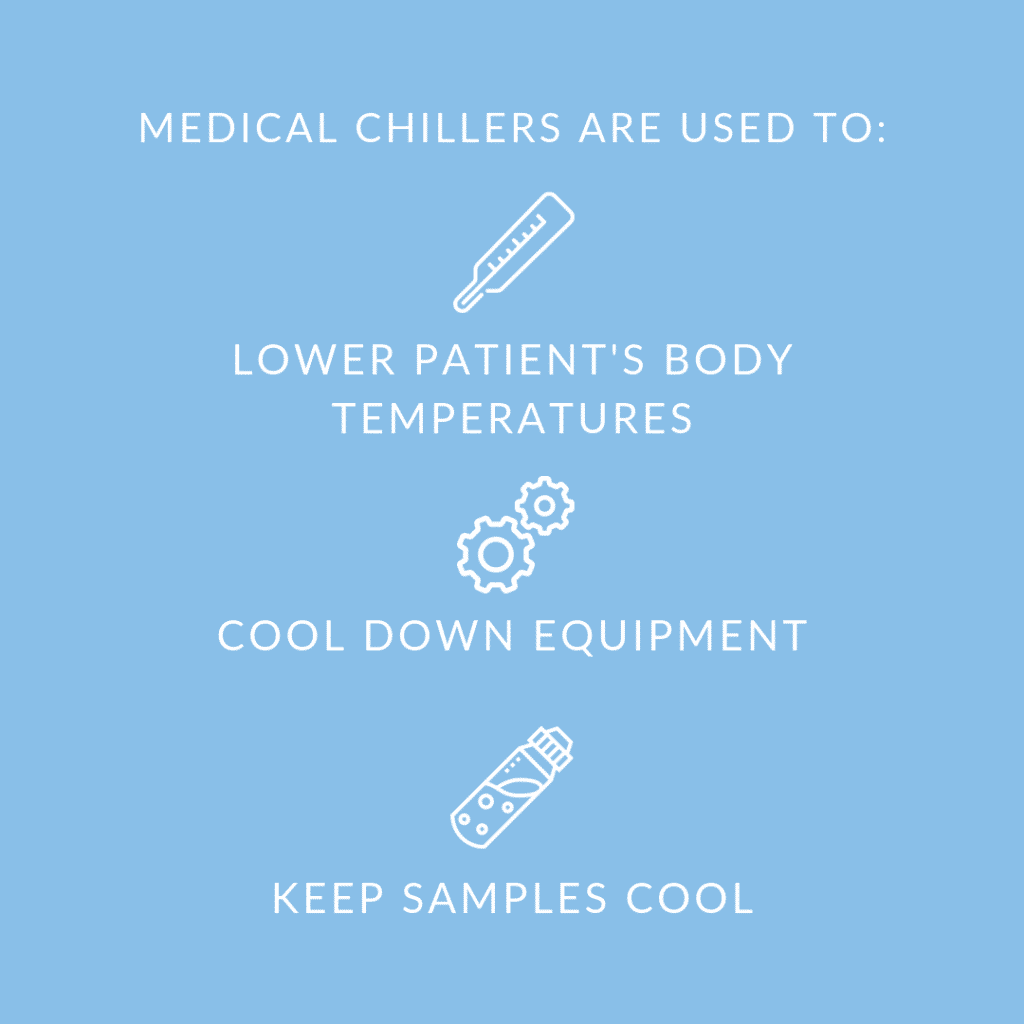
- First chillers are used in medical applications to remove heat from a patient’s body during certain procedures,
Common procedures that require removing heat from body parts or reducing a patient’s body temperature are: hair and tattoo removal, laser eye surgery and vein treatments.
- Second, medical chillers are used to cool down pieces of equipment that generate large amounts of heat.
MRI machines, PET and CT scanners, lasers, x-ray machines, and linear accelerators, all generate significant heat. They require quick cooling to operate for an extended period of time.
- Third, chillers are commonly used to keep sensitive medical samples (i.e. blood samples) at ideal temperatures.
These types of chillers are commonly found in labs where medical testing is performed.
Medical Equipment Chillers
Let’s take a closer look at the mechanics of some medical equipment that require chilling and how medical chillers are used to keep the equipment cool.
MRI Machine Chillers
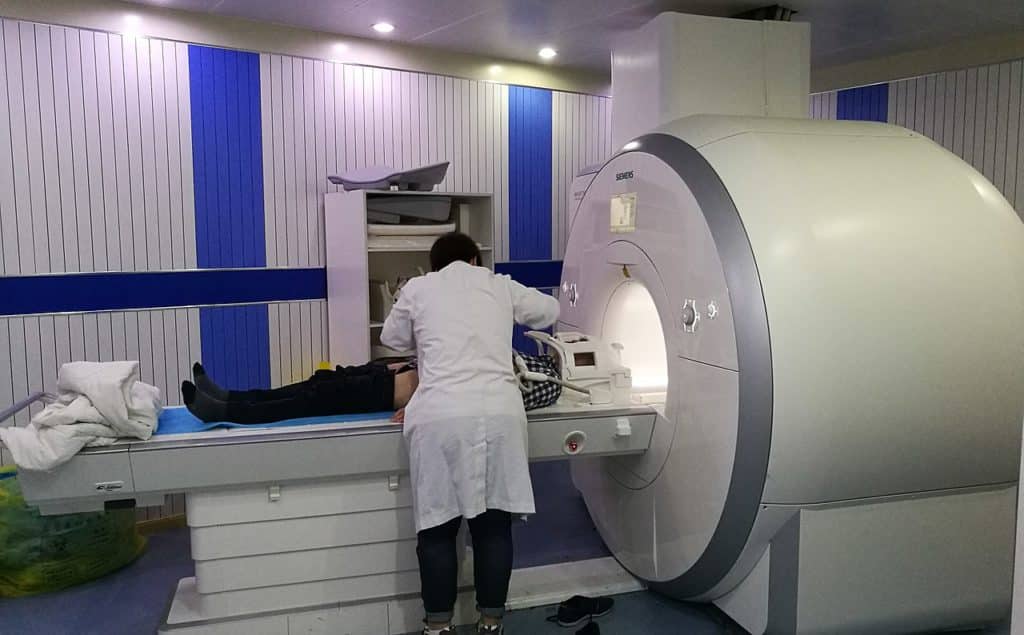
Patient being positioned for MR study of the head and abdomen.
MRI machines use a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the inside of your body
.The magnet inside MRI machines has to stay cool in order for the machine to work efficiently.When it overheats, the magnet and, consequently, the MRI machine, will stop working properly.
Either air or water-cooled chillers are used to transfer heat from the MRI machine. Water-cooled chillers transfer heat to process fluid that is recirculated and air-cooled chillers transfer heat to the ambient air.
CT Scanner Chillers
Doctors use CT scans to look at blood clots, tumors, bone fractures, and more. CT scanners contain an x-ray tube that heats quickly and requires 10 to 30 minutes of cooling time. This cooling time delays patient care and increases medical costs.When this excess cooling time is eliminated via medical chillers, medical facilities are able to help more patients.
PET scans
PET scanners produce three-dimensional images of body processes. Their operation generates too much heat for the scanners to continue operating without a cooling solution. Heat must be removed to keep the machines from malfunctioning.
Linear Accelerator Chillers
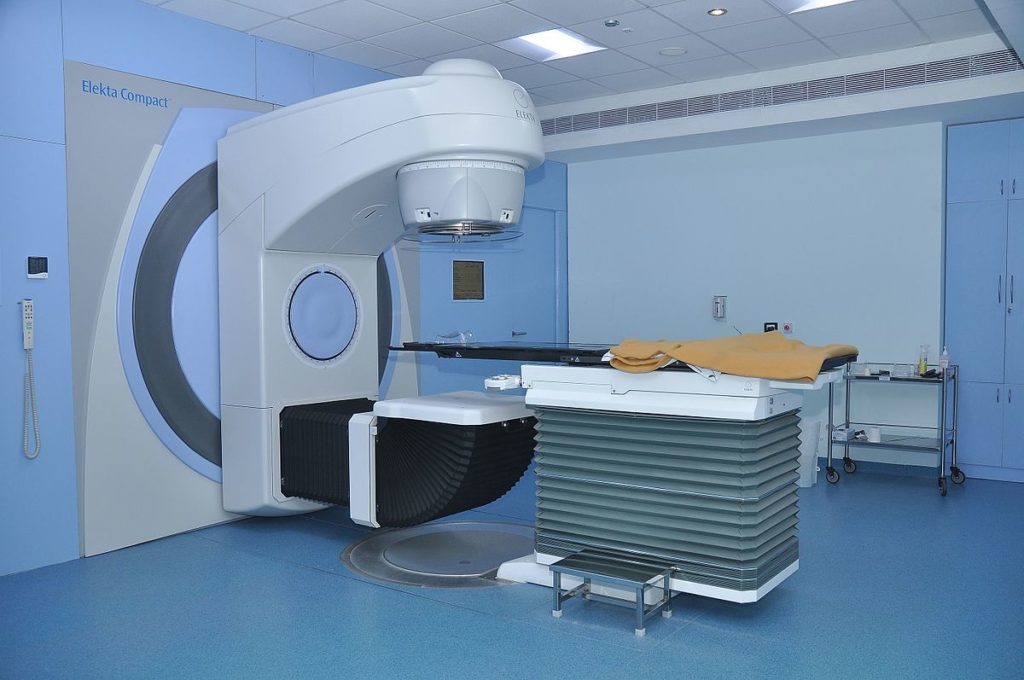
Linear accelerators are most commonly used for external beam radiation treatments for patients with cancer. These machines deliver high-energy x-rays or electrons to the region of the patient’s tumor. The x-ray tubes, however, create large amounts of hear. The tubes require a non-stop cooling solution to function properly.
Medical vs. Regular Chillers
Medical chillers will operate similarly to any other air or water-cooled chiller. (For more information on how chillers work, check out this blog article).
Medical chillers are somewhat unique, however, in that they are not cooling a constant operating load. Their demand is very cyclical; unlike most process cooling applications, the load ramps up quickly and then dissipates equally as fast.
Medical chillers must be able to handle the immediate shock of a load surge and maintain proper cooling for the duration of the load.
Cooling solutions from North Slope Chillers
Chillers from North Slope chillers are durable, reliable, and customizable for any application. You can take a look at our product offerings here.

