Plastic Injection Molding Touches Our Lives Every Day
Products created by plastic injection molding are all around us, from water bottles to the button on your shirt. This process is efficient and can create products that are very large heavy-duty to products that are tiny and delicate. This article explores the top level of all there is to know about the plastic injection molding process.
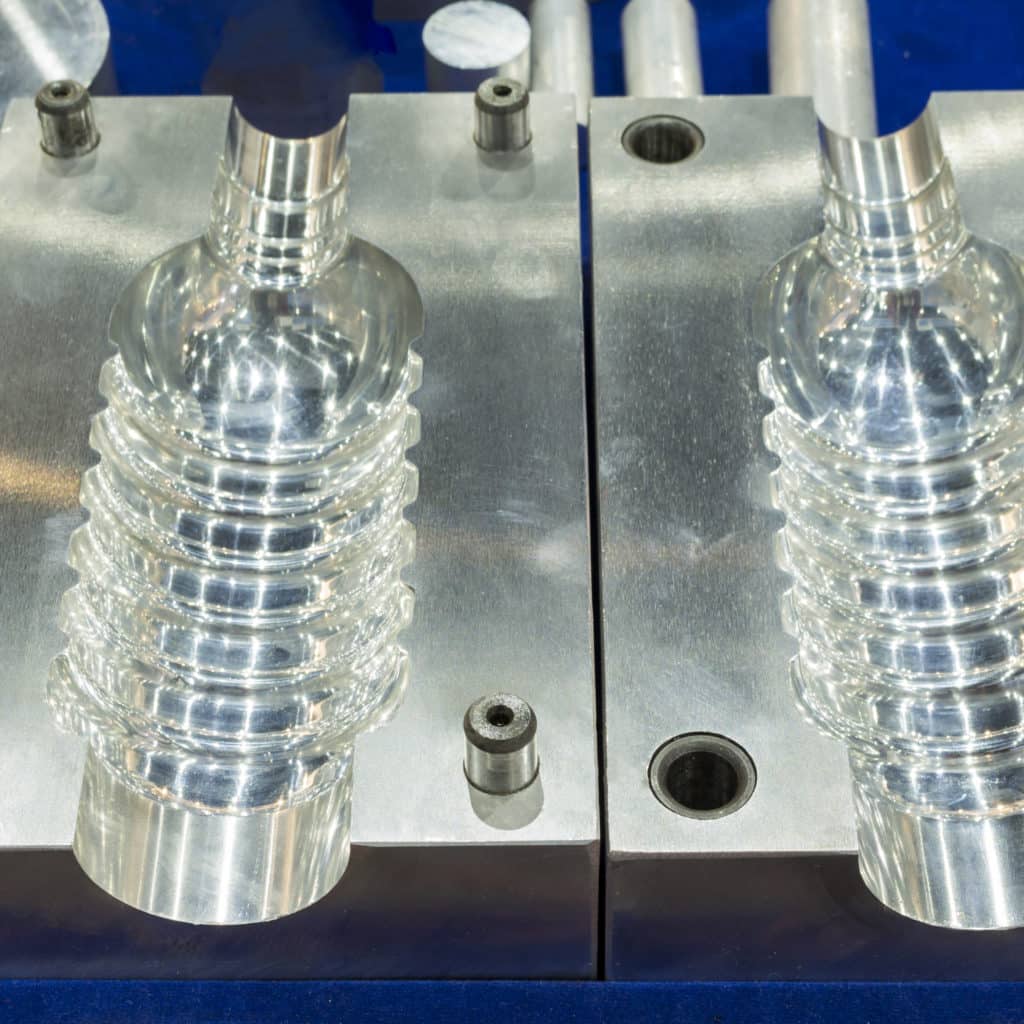
Let’s Learn about Plastic Injection Molding
*Note to reader: American English has no mould, and British English has no mold. In other words, the word referring to (1) the various funguses that grow on organic matter or (2) a frame for shaping something is spelled the same in both uses, and the spelling depends on the variety of English. For the purposes of this article regarding plastic manufacturing, I will be using the American English version.
Standard household items, produced every day, are the result of injection molding. The applications cover commercial, industrial, and consumer products. Because of injection molding manufacturing, companies can design products that are intricate, versatile, and complex, and also range from very small to large objects.
This method has produced solid parts such as electronic housings, bottle caps, containers, computers, televisions components, outdoor furniture, agricultural products, toys, machinery components, and much more.

We Use It: Common Products Made with Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic bottles are the most common product manufactured by the billions each year. Plastic bottles are made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), because the material is both strong and light.
Electronic housings used in devices such as remote controls, computers, televisions, medical equipment, and other consumer electronic components, are all produced by injection molding process.
Toys: Toys need to be lightweight, durable, and corrosion-free. Lego is a perfect example of an injection mold toy. A firmer plastic granule is heated until liquified and then injected into metal molds. After cooling, that heated plastic becomes one of the world’s favorite toys. Lego is a precision product that must fit together perfectly–manufacturing must be perfectly executed.
Quick List of All the Places We Find Injection Molding Products
Automotive:
- Color-matched Interior Components
Commercial Construction:
- Conduits for Concrete Beams
- Insulators
- Raised Flooring Panels
Residential Construction:
- Roofing Vents
- Railing Gaskets
- Deck Fasteners
Commercial Products:
- Electrical Boxes
- Mop Heads
- High-end Trash and Recycling Receptacles
- Vending Machine Components
- Equipment Housings
Consumer Goods:
- Skateboard Storage Racks
- Barbecue Accessory
- Bird Feeder
- Tackle Boxes
- Toilet Seats
Food Service:
- High-Temperature Serving Pans
- Bread Trays
- NSF Food Service Products
Home Products:
- Flower Pots
- Wire Ties
- Air Freshener Units
Medical Components:
- Sharps Disposal Bins and Wall Mounts
- Medication Trays
Toys and Hobbies:
- High-end Collectible Models
- Decorated Children’s Furniture
POP (Point of Purchase):
- Spring-loaded Supermarket Display Tray
- Literature Display Rack
Sporting Goods:
- Training Device
- Exercise Tools
Short-Run 3D Printed Components:
- Electrical Knobs
- Specialty Buttons
- Fixtures
Good to Know
First, the Mold
Injection molds must have a high precision match between the two mold halves in order to perfectly control the material flow. Creating the mold is crucial to building a seamless, precision product. Injection molds are typically constructed using steel or aluminum, and precision machined to form the features of desired product.
The mold must be:
- Sturdy and able to withstand the pressure involved during injection.
- Made of materials that the polymer will properly flow along.
- Carefully designed to allow heat transfer to control the cooling process.
Over and Over
Once a funcional and errorless mold is produced, the injection molding process is fairly repetitive. It also has a low scrap rate (percentage of failed assemblies or material that cannot be repaired or restored, and is therefore condemned and discarded) relative to other manufacturing processes.
Advantages
Repetition and reliable high volume production is the signature advantage of this process. Once the first part is produced, the second is going to be practically identical. Other advantages are the wide range of material selection, low labor costs, minimal scrap losses, and few requirements for post-molding finishing operations.
Disadvantages
The major disadvantage of injection molding is the initial cost of the mold design, which tends to be high due to design, testing, and tooling requirements and the longer required lead times. Some custom complex parts may encounter problems during the injection molding process such as warpage or surface defects. Therefore, injection molded parts must be designed with careful consideration to any change in geometry as they cool and the material selection to ensure stability.
The Injection Molding Process
Injection moulding involves a high pressure injection of a polymer into a mold where it is shaped. The individual parts of this process are very short. The whole injection molding process usually lasts from 2 seconds to 2 minutes, and is yet, highly complicated. There are four stages in the cycle. To watch an excellent animated video on the Injection Molding Process CLICK HERE.
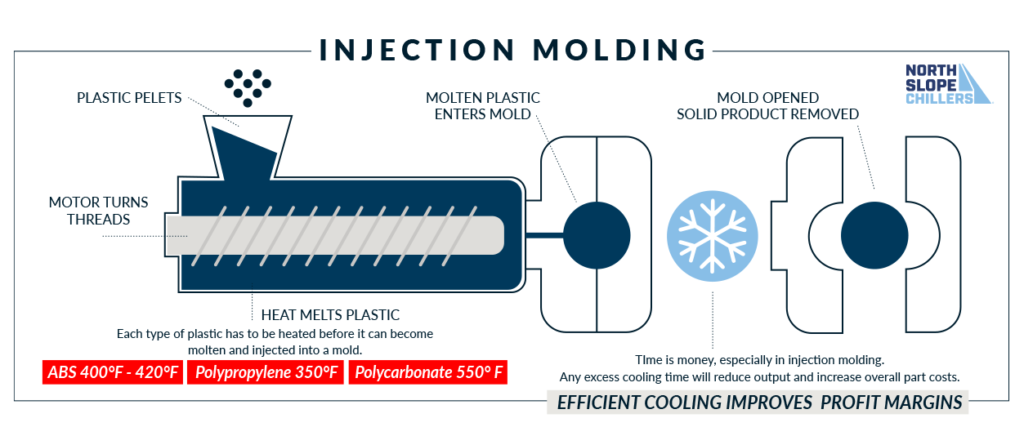
Clamping
Before the mold is injected with material, both halves must be closed. The clamping unit takes care of this. Both halves (the cavity and the core) are then secured in the tool. Material is then injected as the clamping unit pushes the halves together and both halves are held tightly while material is injected. Larger machines (machines with more clamping power) take longer to close and clamp the mold.
Injection
A hopper feeds plastic pellets into the injection mold machine. Heat and pressure melt the pellets and help the transformed plastic move through the injection unit. The volume of injected material is called the ‘shot’. Injection is complete when 95%-99% or the mold is filled. It is hard to calculate exactly the injection time because the flow of the plastic is always changing and dynamic. Injection time can be estimated by other factors such as injection pressure, power and shot volume.
Cooling
Cooling is when the plastic within the mold hardens. This process begins as soon as the plastic makes contact with the interior mold. During cooling, the part may shrink slightly. The mold should not be opened until cooling is complete. Cooling times are estimated based upon the wall thickness of the mold and the thermodynamic properties of the plastic.
Ejection
Now, the product must be removed. An ejection system is used because force is required to remove the product. The product will shrink and stick to the mold. Once removed, the mold is shut, and the process begins again.
Injection Mold Manufacturing Machines
The machines are differentiated by the type of driving systems they use: hydraulic, electrical, or hybrid.
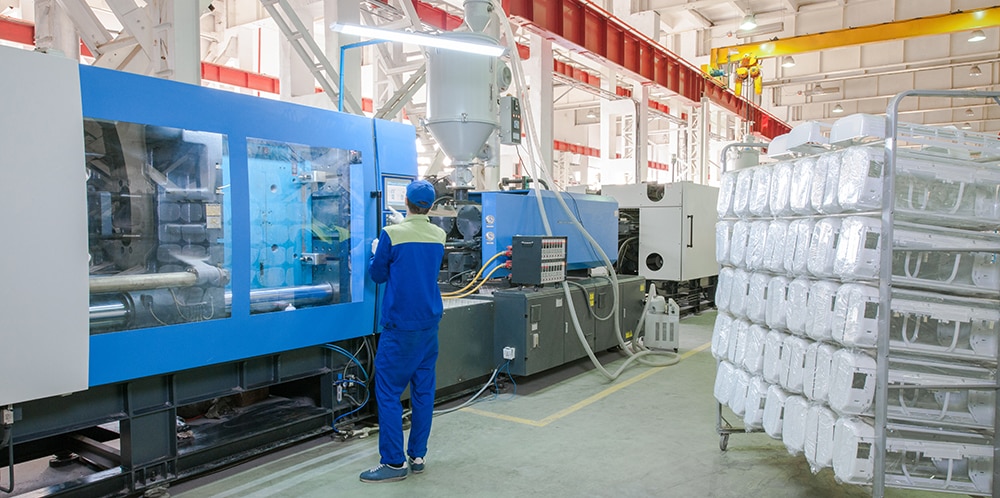

Hydraulic
Hydraulic presses, until 1983, were the only option available to molders. Hydraulic machines, although not nearly as precise, are the predominant type in most of the world. These systems use hydraulic cylinders that clamp the mold halves together, with enough force that the mold will remain shut and sealed during injection – between three and four tons of clamp force per square inch are generally required–sometimes more. Modern hydraulic injection molding clamps can exceed 8,000 tons of pressure, allowing them to create parts in excess of 50 pounds.
Advantages:
- Higher clamping force for large parts, plus larger shot size
- Resistance to wear and tear
- Excellent injection rates and ejection capabilities
- Lower initial purchase price
- Low cost and great availability for replacement parts
- Gas accumulators available to help account for slower clamp movements
Disadvantages:
- High energy consumption, even while idle
- Higher required molding temperatures and therefore longer cooling times
Electric
In 1984 an all-electric injection molding machine was introduced in Japan – it took a bit of time, but these systems are now popular all over the world. The electric press, also known as Electric Machine Technology (EMT), reduces operation costs by cutting energy consumption. Electric presses have a reputation for being quieter, faster, and having higher accuracy, however electric machines are more expensive.
These systems utilize digitally-controlled servo motors for their power rather than hydraulics, meaning that they can bring faster and more repeatable processes with more precision and efficiency. Once you pinpoint a given process within your system, it can be replicated consistently with ease, allowing for the creation of bulk projects for a variety of major industrial applications. These systems can also run unattended, which lowers labor costs.
Advantages:
- Precision and ease of repetition, along with low scrap rates
- Lower down time than hydraulics
- Cleaner processes with no fluid leaks
- Major energy savings
- Less noise and faster operation with a shorter startup time
- Lower unit cost and less material waste
- Lower power requirements that lead to lower operating costs
Disadvantage:
- Cannot achieve the clamping force of a hydraulic system
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid injection molding machines (sometimes referred to as “Servo-Hydraulic”) are meant to combine the benefits of hydraulics and electrical systems. These systems have the high clamping force of hydraulics, and combine that with the precision, energy savings and reduced noise associated with electrical systems.
Advantages:
- Electrified screw rotation that limits screw recovery needs
- Diversity in product design capability
- Reasonable costs (lower than electric, higher than hydraulic)
- Continuous adjustments by the servo pump
- Closed loop processes with a faster response time
- Lower temperatures required for limited cooling times and extended machine life
Hybrid machines are used for a variety of wall thickness needs, including heavy industrial projects.
Injection Mold Process Cooling
There are two main reasons for using a chiller for the injection mold cooling process.
- Protect Equipment: While the chiller represents a small cost of the processing equipment, it provides solid protection of your investment, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week for years and years to come.
- Increase Production: Maintaining a constant and proper cooling temperature in equipment will increase the number of parts produced per hour, and a significant reduction in the number of defective parts.
Cooling is a critical stage in the process; over 80% of the total plastic manufacturing process is devoted to cooling. An injection molding chiller will drastically reduce the cooling time and preserve the quality of your products.
North Slope Chillers industrial liquid coolers are the best way to consistently and efficiently maintain life of your equipment and the quality of your plastic parts while also reducing your production time.
Contact us to find the right temperature control solution for your needs:
(866) 826-2993 [email protected]

