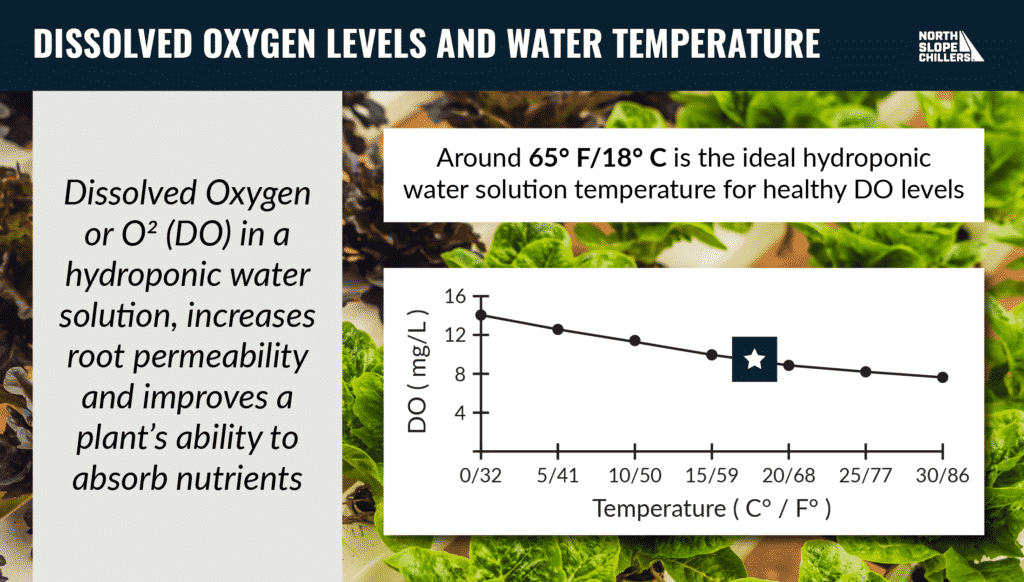
What Are Heat Exchangers?
A heat exchanger is a system that transfers heat between substances, through the movement of a cooling medium (fluid or air). They are used for both heating and cooling in a wide range of industrial applications: power stations, computer processors, chemical plants, food and beverage processing, refineries, refrigeration, space heating/cooling, combustion engines, and more.
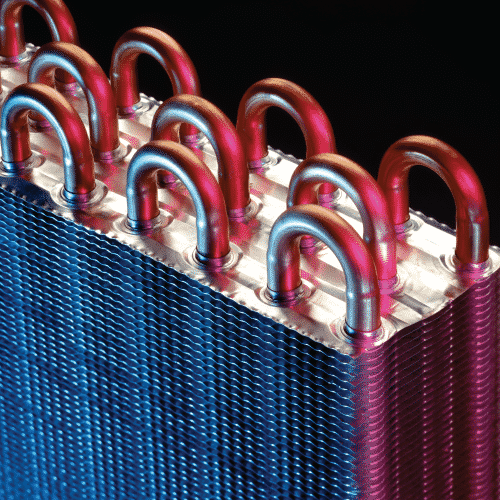
Biological Heat Exchangers
Some of the most influential inventions come from observing natural phenomena. Heat exchangers are no different, as they are present all across the planet, including the animal kingdom. In fact, you are breathing through one right now. As you inhale cool air through your nose, warmth is transferred from nasal passage blood vessels into that air, and you exhale warm air. These circulatory system heat exchangers are also found in animal ears, limbs, and even special organs (called the carotid rete) to help regulate body temperatures in extreme environments.
How Do Heat Exchangers Work?
Heat exchangers use the principles of thermodynamics to move heat away from (cooling) or into (heating) an area as efficiently as possible. Here, there are 3 main methods of heat transfer at play: conduction, convection, and radiation.
Heat Transfer Methods
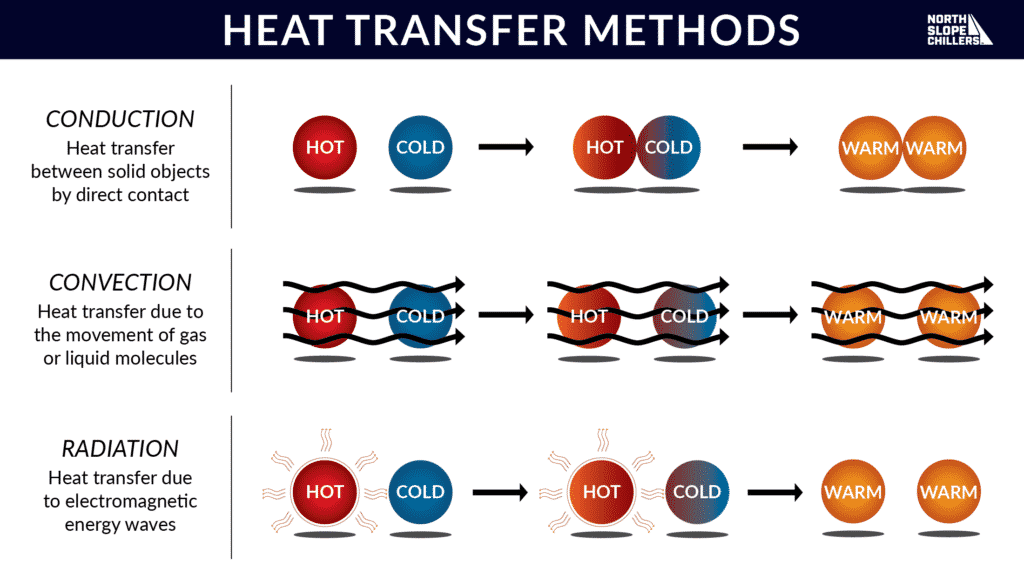
Conduction requires physical contact between solid objects in order for heat to move. A simple example would be a pot on top of an electric stove. Heat is directly transferred from the stove into the surface of the pot. Now to see convection in action, imagine you fill the pot with water. Heat will circulate and move through the liquid molecules so that even the water molecules in the very center of the pot get hotter. The easiest way to understand the process of radiation is to walk outside into the sunshine. Electromagnetic waves from the sun are radiating down on us every day.
Maximised Surface Area Contact
Using the diagram above, we can see that contact and movement are important heat transfer factors. That means we can improve heat movement with greater surface contact, contact time, and efficient flow. Simply put, greater surface area contact + longer contact time + continuous flow = greater heat transfer. The faster and more efficiently heat is moved, the better. Heat exchangers accomplish this by maximizing both surface area and contact time with a flowing cooling medium (either air or fluids).
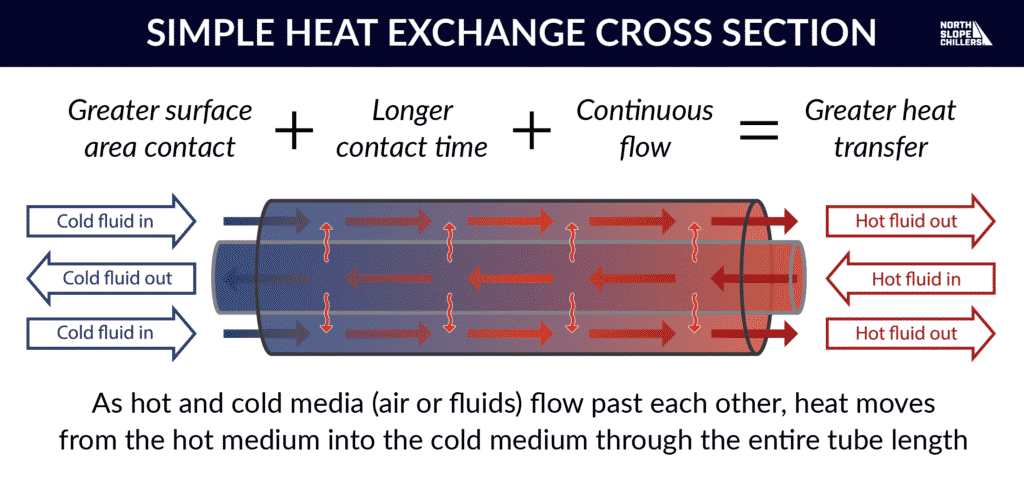
As hot and cold media (either air or fluids) flow past each other, heat moves from the hot medium into the cold medium for as long as they are in contact with one another. Heat exchangers are specially designed to maximise this contact as much as possible within the space provided. Let’s take a look at some of the clever designs used in heat exchangers today.
Types of Heat Exchangers
There are many ways to make and hot and cold media flow past each other. Thermal engineers will use different set ups depending on the thermal load (how much heat needs to be moved and how quickly) for different applications. Using these designs elements, there are an infinite number of possible combinations and flow paths.
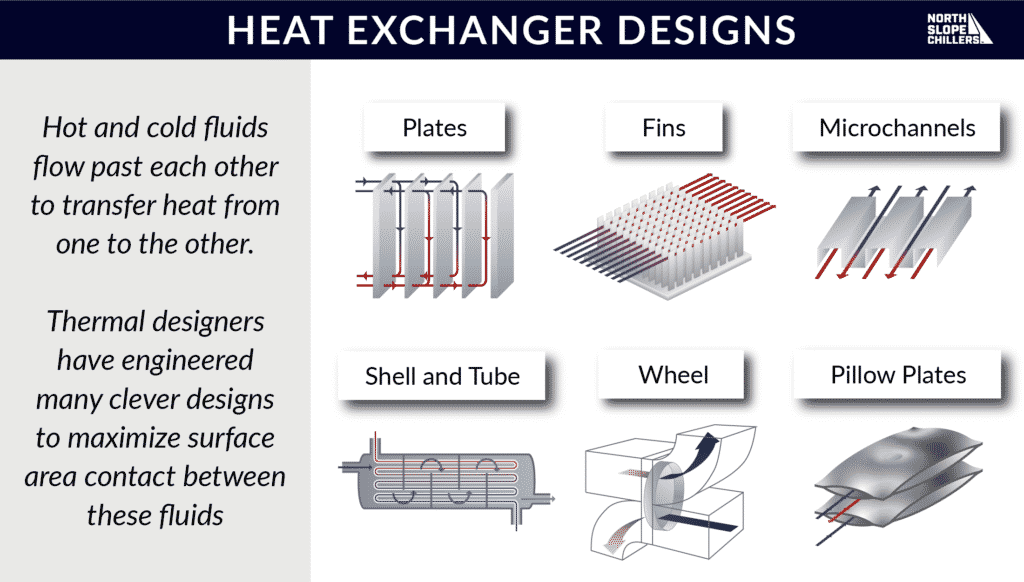
Plates
Some heat exchangers use metal plates that are stacked or lined up in a row. Hot and cold media flow over these plates in an alternating pattern to transfer heat.
Fins and Microchannels
To further increase surface area, these plates can also be textured with microchannels or fins to produce additional flow paths. Instead of flowing uniformly over the metal plate’s surface, the fluid flows along these strategically organized paths.
Shells and Tubes
In this model, tubes of fluid enter a shell filled with an alternate fluid temperature. The tubes perform a series of bends and turns inside to increase contact with the alternate fluid. During its time in the shell, the tube fluid either transfers or receives heat from the shell fluid.
Wheels
This heat exchanger is most commonly used for HVAC applications. Ductwork channels direct outside air and inside air past one another and the exhausts are directed out the other side.
Pillow Plates
Pillow plates are a series of metal plates that are welded together in certain spots to create negative space pockets. A metal plate will have many weld locations and many empty negative spaces in between. 1 fluid flows through those negative spaces, while the other flows in between the pillow plates.
Quality Interior Components from North Slope Chillers
At North Slope Chillers, we know that a chiller is only as good as its heat exchanger. Our powerful and portable industrial chillers are crafted with the best internal components for reliable high performance to efficiently remove waste heat from materials, equipment, and industrial processes. Our chillers are equipped with brazed plate heat exchangers (copper brazed stainless steel) that provide both compactness and heat transfer efficiency. For applications that require deionized chilling, we used brazed nickel heat exchangers to protect you from corrosion. With a wide range of chilling capacities, we can match the exact thermal load of your application. Contact us to find the right industrial chilling solution for your needs at (866) 826-2993 or [email protected]